Natural Language Processing is here, and it’s here to stay. With algorithms like BERT and MUM, Google’s understanding of search queries has never been better and those of us in SEO need to draw level.
We’ve assessed how useful NLP really is and are here to tell you how it can be implemented to create effective, high-ranking content.
Keep reading to find out how NLP is more than just a techy term for SEOs. Used in the right way, it’s the key to those sweet first-page spots.
So, what is NLP?
Natural Language Processing applications, in short, help computers better understand human language. Users are evermore specific about what they want to find, and Google has had to adjust and improve to meet this. 15% of search queries are used for the first time, and now, users can even use voice-search to get their query across. NLP helps Google to decipher the request, no matter how bizarrely-worded. Site Centre shared these stats showing us just how much Voice Search is taking off:

Source: Site Centre
NLP isn’t particularly new. In 2015 Google launched RankBrain, their first artificial intelligence method for understanding queries. But in the past few years, there has been an influx in new NLP applications. It’s now pretty much everywhere, on your search engines, translators, the Alexa you have at home. We’ve got Word2Vec, CBOW, MUM, BERT and countless other efforts to make sense of human lingo.
I’m going to take you quickly through BERT and MUM, and how they can change your SEO game. Launched in 2019 by Google, BERT immediately impacted 10% of all search queries and is said to be the most critical advancement in search in many years. It is an NLP technique and the first to rely completely on self-attention mechanisms.
In their report, Google used this example to demonstrate how BERT is helping them grasp the nuances of users’ queries:
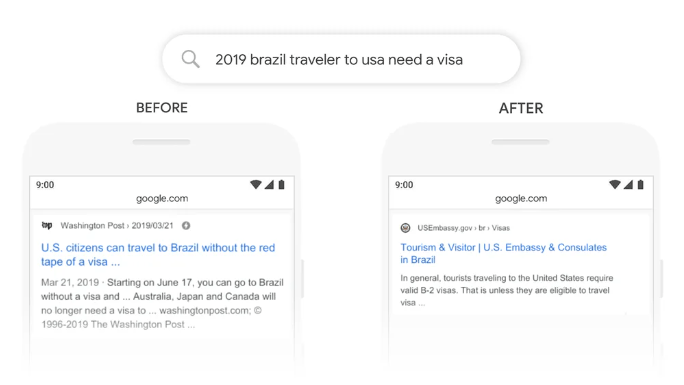
Source: Google’s report on BERT
As you can see, NLP means that Google can now work out that this search is about a Brazilian traveling to the US, not the other way round. BERT just means that those little words like ‘to’ don’t get lost anymore when interpreting a query.
In May 2021, Google introduced MUM as a 1000 times more powerful evolution of BERT. It’s not quite as scary as it sounds, essentially it just makes Google search even more semantic and context-based. It’s specifically looking to improve international search, and improves on BERT by being trained in 75 languages. For more information about the MUM update, see this article.
How to implement NLP for SEO:
So this is all well and good but how can we utilize these exciting new algorithms for our clients? To make this guide nice and easy to follow, I’m going to break it down into a few top tips:
Write content for users (it’s not me, it’s you)
NLP means that Google is getting better at understanding natural language. Writing content for users has always been important for SEO but it is now more important than ever.
Your content needs to be simple and clear to be optimized for these algorithms, and deliver a good user experience. When you’ve finished writing, take a step back and check that it all makes sense. Determine what a searcher’s intent is and write content to match. This article will give you some hacks about how to go about this.
But…keep it specific (a matter of semantics)
With BERT and other NLP applications, Google has attention to next words, previous words, and related words in a sentence, in something called Semantic Search. Google understands the tonality now, and the specificity of the query. Alongside this, we are seeing a rise in long-tail keywords, because of things like Siri. Therefore, get more specific and descriptive with your content, whilst keeping it simple.
Check out this diagram showing the dominance of the long-tail search.
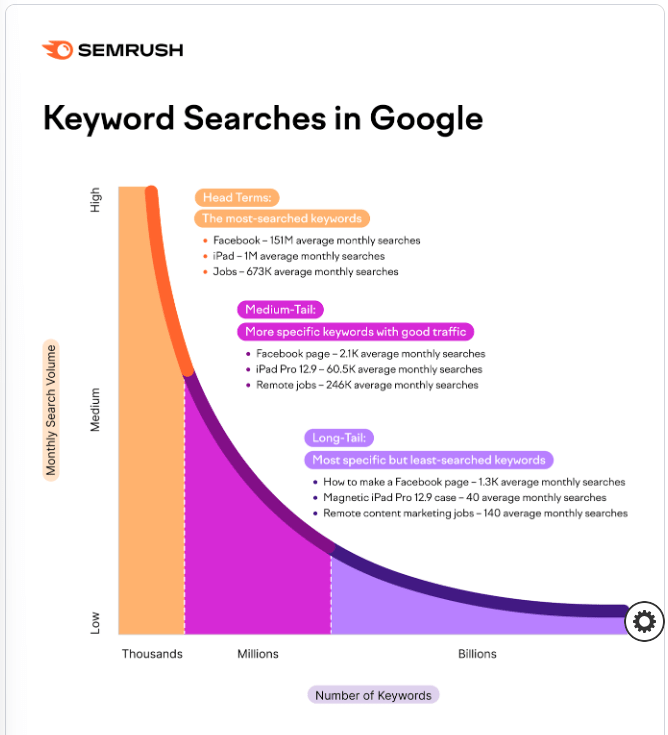
Source: Semrush
Think back to the last thing you typed into Google – it was probably a long-tail wasn’t it? Essentially, Google is understanding these descriptive queries to a much greater extent now, so our content needs to be equally as specific.
Structure is key
Coherently written copy is useless without a clear structure. Once you’ve written your information, make sure it’s structured in a way that allows NLP to understand it. This article on Google’s Knowledge Graph explains how it’s easier for Google to understand structured data, than unstructured.
Use headings such as H1 and H2, using similar keywords in both. Then, utilise subcategories to further break up the content. This will all make the information easily scannable, and ranking better as a result. We’ve got more in-depth information here about structure, if you’re looking for a blog to help you tackle on-page SEO specifically.
It’s time to get sentimental
A key feature of BERT is its analysis of the Sentiment of a query or a webpage. Sentiment is the undertone of the content and it can be positive, negative, or neutral. It also exists on a -1 to +1 scale.
-so in layman’s terms, positive sentiment would be positive words like “the medicine is awesome, it really works, it alleviates pain, and it’s affordable too.”
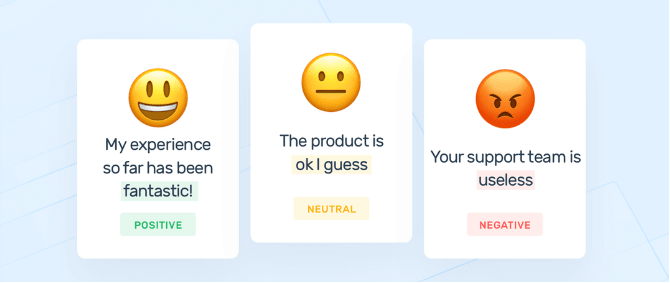
Source: Monkeylearn
Why should we care about Sentiment in SEO? Well, if all the results on page 1 are offering positive sentiment and your page has mostly negative vibes, there is a strong chance Google will not consider the page relevant to what the user is looking for. So no high-ranks for you! When optimising content for your clients, you need to make sure that you’ve done your sentiment analysis. It can be used to create more relevant content that lines up with the user’s expectations. Google has a useful tutorial here for Sentiment Analysis.
On the other hand, it can be used to identify any negative or neutral content on the website that might be turning off potential visitors. This information can then be used to strategise updates for the content – improving user experience and search engine ranking. For example, one particular product might be getting lots of bad reviews and sentiment analysis can help you detect this.
Links, links, links
Thanks to NLP, link structure and placement are even more crucial. As mentioned above, content needs to be relevant and equally, you can’t just place a link randomly on a page. Every link needs to make sense to the content. I know we all love our links in SEO, but they can’t just be shoe-horned in. Make your anchor text contextually relevant to the page – with the right context it will have full value.
If there is additional information about something elsewhere, it’s a great idea to link to it because this gives your page extra validity. However, with NLP it is super important to avoid non-descriptive anchor text. Aim to include a range of natural keyword variations and natural language pointing to your target page. Of course, you also want other pages to link to your page, so, once again, keep that content relevant!
Take a look at this guide we put together explaining how to create an effective internal linking strategy for SEO.
Ask away
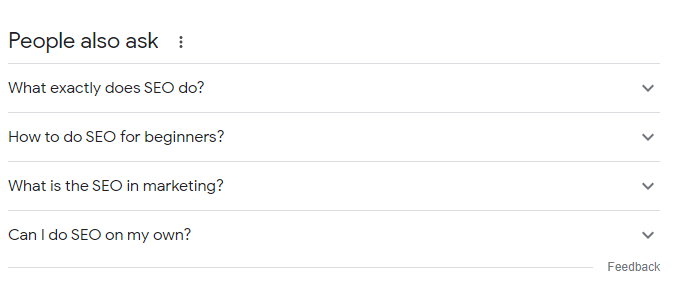
Information from Google Patents states that your content is more likely to be selected for the ‘People Also Ask’ answers if it’s presented as a question and answer.
Think about it, NLP is making Google better at understanding human queries. These queries often include questions, so we need to use this language in our content. Ask the questions in your copy that the user would ask, and then answer them straight after.
By using complete questions in your SEO content, you signal that your website is providing comprehensive answers to a specific question. So now you understand my use of questions in the article you’ve just read!
Keep your friends close but your *competitors* closer
Steve Bailey, Head of Technical SEO at Spike Digital, says that “the biggest risk with focusing on NLP is not doing your research”. Whilst analysing your page is vital, it is equally important to scope out the competitor pages. This helps you build a more well-rounded sense of the impact NLP is having on your sector.
You can use NLP to analyse the top ranking pages and the metrics that now matter (like sentiment, entities and salience). Make sure that your on-page content is similar and then you can expect to rank just as high.
Google’s API Demo
On the subject of analysis, Google’s natural language API demo can examine any text for free. It comes back with a whole heap of data for you, which can then be compared to the highest-ranking pages.
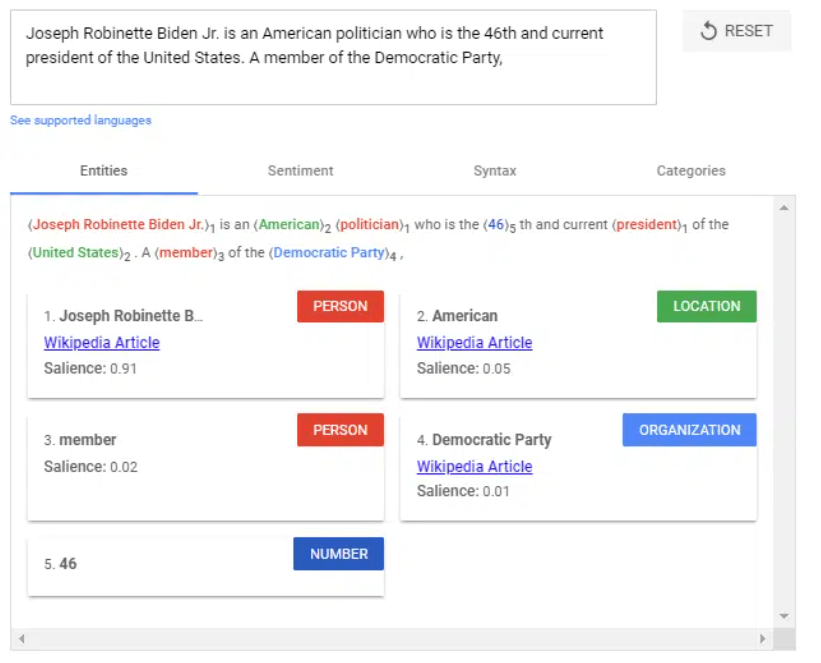
Here’s an example of the API demo in action, you’ll see that it identifies ‘entities’ for you.
An entity is a word or phrase that represents an object which can be identified, classified, and categorised. For example, this might be a person, event or number. NLP selects and evaluates entities, scoring their salience (how important they are in the text).
So, by taking a look at analysis of entities and salience in your content, and that of your competitors, you can determine how your content can be optimised.
To summarise
With NLP taking off, we need to work more than ever to match user intent in our SEO. Semantic search is an absolute game changer. We need to keep NLP in the back of our minds at all times as SEO content writers -it’s here to stay but it should be embraced. The traditional ranking factors like keywords still matter, but new factors like sentiment must be considered.
Now that you know about Google’s new metric system, use it to your advantage. Go away and analyse your pages, your competitors pages and even our pages if you’d like!
I’ll leave you with a final run down of how to make that content completely irresistible to NLP:
- Keep it specific and coherent
- Use structure to your advantage
- Match user sentiment
- Employ internal and external links
- Anticipate the user’s questions
- Get analysing









